IELTS Reading: Task 9 – Diagram Label Completion
For this task, test takers are to label specific parts of a diagram, plan, technical drawing (a machine), or something found in nature. You must select words from a text that discusses the diagram or from a list of words in a box to fill in the blanks found in the diagram. You may have to be aware of paraphrasing and synonyms. You must read the instructions to know how many words you are allowed to write in any one blank.
Note: Hyphenated words count as only one (1) word (“ugly-dirty” streets)
Some diagrams look difficult but they are generally easier than other types of questions. Some diagrams even include a glossary that defines difficult words. Test takers do not need to know anything special to do complete a diagram – all the information needed is in front of you. Usually, you have to deduce the meaning of the information given: whether these are numbers, the heading of a column, a completed part of the diagram, or some text–all can give you clues as to what is needed to fill in the blank in the diagram.
Note: always fill in the blank, even if you have to use an educated guess.
Some blanks will be easier to answer than others, so you can always do the easier ones first and then study the diagram again to winnow down the correct possible choices.
Procedure:
1. Read the instructions. Usually, General Training exams will have test-takers choose from a list of words, whereas Academic tests will more than likely have test-takers read through a text of several paragraphs to fill in the blanks.
Note: Answers will not follow the same order as the text or box list.
- Know the number of words allowed to fill in the blanks.
- Observe the diagram and look for clues in the column headings and any other information available
- Scan the text looking for keywords that surround the blank you are trying to fill or look at the box of words and attempt to eliminate choices that do not fit or are not suitable for the particular blank.
- Read the section in the text that is applicable to locate your answer.
- Fill in the answer according to the instructions–ensure your spelling is correct.
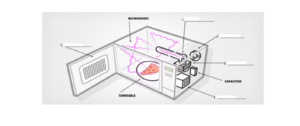
Complete the diagram below.
Use NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the text.
Write your answers in boxes 1 – 5 on your answer sheet.
Spector, D. (2014, June 10). How does a Microwave Work? Retrieved June 15, 2020, from https://www.businessinsider.com/how-do-microwaves-work-2014-6
A transformer, located underneath the magnetron, converts standard household electricity of 120 volts to around 4000 volts or higher to power the magnetron, the component inside the microwave oven that generates microwaves from electricity. The voltage heats a filament at the centre of the magnetron that boils off electrons. The electrons are whirled around by two ring magnets. This creates microwaves at a specific frequency, typically 2.45 gigahertz. Then the microwaves are transmitted into the cooking chamber by an antenna, located just above the magnetron. The microwaves bounce around inside the cooking compartment eventually penetrating the food and heating it up. The microwave door contains a metal mesh with holes that are small enough so that microwaves can’t escape but visible light can, so we can see inside. Most microwaves have a revolving glass turntable that moves around like a carousel, so it heats evenly. A microwave rarely overheats unless it is left on for an extended amount of time. However, there is a fan at the back of most microwaves that aids in cooling the unit.
Answers:
- Antenna
- Fan
- Magnetron
- Transformer
- Metal Mesh

